HANA (High Performance Analytic Appliance) is the new application platform from SAP. It contains a column-based in-memory database and a variety of services. SAP HANA was introduced in 2011 as an in-memory platform, heralding the onset of the new SAP HANA era. Because earlier relational databases were no longer capable of managing the ever-increasing requirements of SAP customers, transactional processes (OLTP) and analytical processes (OLAP) were needed. In the past, two databases were required for this particular scenario.
In-memory technology
In-memory technology is the basis of SAP HANA. With this technology, data are no longer transferred from a hard drive to the RAM. Instead, they constantly remain in the main memory. This eliminates transfer to the RAM and the necessity of indexes and temporary tables, making systems run much faster. The parallel processing of this new database technology also increases data throughput and analysis speed many times over and makes it possible to process and analyse large quantities of data (Big Data) practically and in real time.
The SAP/4HANA database’s in-memory technology has been useable on the market since 2011. In 2013, SAP announced that the majority of SAP Business Suite core applications and industry solutions were available on the basis of SAP HANA (“SAP Business Suite on HANA”), completing the changeover from the SQL database previously in place to SAP HANA. SAP S/4HANA has been available as an SAP HANA-based complete solution since 2015.
Comparison of data storage devices
| HDD | SSD | RAM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data rate | 160 Mb/s | 500 Mb/s | 25 Gb/s, 25000 Mb/s |
| Access time | 7 ms | 0,3 ms | 60 ns, 0,00006 ms |
| Data rate factor | 1 | 3 | 156 |
| Access time factor | 11500 | 5000 | 1 |
Faster access through new database architecture
Another new feature is the conversion of the database to columns. Most relational databases store data sets on a line basis. This is a consequence of the original requirement to depict transactions such as order postings. SAP HANA stores all data sets on a columnar basis, making much greater compression possible. Double-entries only occupy one section of the memory, which also reduces the amount of memory required.
Comparison of OLPT/OLAP
| OLTP | OLAP |
|---|---|
|
|
What else can SAP HANA do as a database?
SAP HANA is more than just a database. It also provides a variety of services, including Application Services, Processing Services, Database Services, and Integration & Quality Services. In the SAP database, applications can be programmed in different programming languages. The database, which can be accessed using open standards such as OData, allows companies to use SAP HANA along with SAP products and system-integrated applications that use the performance of SAP HANA.
In short, SAP HANA provides a platform containing a database with impressive performance and open standards, as well as services that allow for the integration of a company’s own applications.
SAP HANA in the Cloud
Developing FIORI apps on the SAP HANA platform
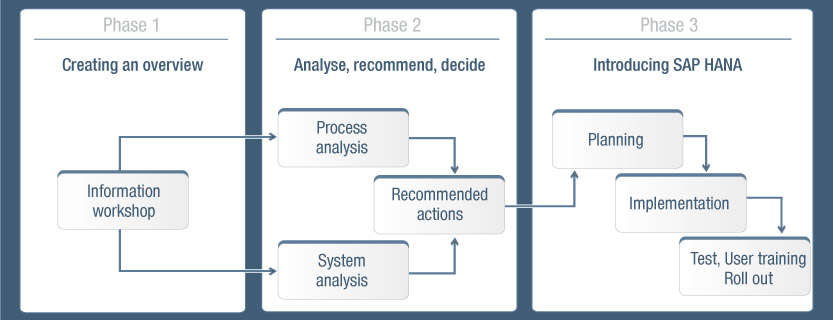
Consultation and service from a single source
Our trained consultants work together with our customers to create solutions that are perfectly tailored to their needs. Personal consultations and specifically assigned contact persons ensure clear communication and the smooth implementation of the entire process.
Information workshop
- Overview of SAP HANA technologies
- Typical business cases for specific departments
- Framework conditions and technical requirements
- Overview of migration scenarios
- Effects on organisation and roles
Recommended actions
- Analysis of benefits in the company
- Actual process analysis
- Actual systems analysis
- Recommended actions
Implementation
- Implementation planning
- Technical installation
- Process implementation
- Tests
- User training